Who Uses UAE Foundations?
We have structured foundations for:
- High-net-worth individuals (HNWIs) use UAE foundations to protect assets from personal liabilities, ensure smooth succession without forced heirship, and reduce estate fragmentation across generations.
- Family businesses rely on foundations to separate family wealth from operational risk, giving them a long-term vehicle to manage generational assets.
- International investors leverage UAE foundations to consolidate and manage global investments, benefiting from the UAE’s tax-neutral environment and ease of international compliance.
- Philanthropists use them as charitable vehicles, as UAE foundations can be structured for social and non-profit purposes while maintaining governance over fund use.
- Islamic families choose UAE foundations to align with Sharia principles while gaining legal certainty and flexibility in estate planning.
- Entrepreneurs and startups increasingly use foundations to hold intellectual property or company shares, protecting assets during early-stage volatility.

Foundation Setup Services Provided By Us
Our Comprehensive Foundation Setup Services
![]()
Consultation
1
Receive expert advice on UAE foundations under DIFC, ADGM, and RAK ICC rules. Choose the jurisdiction best suited for your family’s needs, asset locations, and governance goals—DIFC/ADGM for common law certainty; RAK ICC for cost efficiency.
![]()
Documentation Preparation
2
Prepare all key legal documents: Foundation Charter, Bylaws, Founder’s Declaration, Register of Council Members. Ensure compliance with UAE notarization and Arabic translation requirements.
![]()
Licensing & Registration
3
Register seamlessly with the DIFC Authority, ADGM Registration Authority, or RAK ICC Registrar. We manage filings efficiently to meet UAE legal standards, typically within 1–2 weeks.
![]()
Governance Setup
4
Appoint the correct governing parties:
- Council Members (minimum two for DIFC/ADGM)
- Guardians (mandatory for charitable foundations)
- Registered Agents (required under RAK ICC rules) Ensure alignment with Dubai Land Department (DLD) property ownership rules.
![]()
Bank Account Opening
5
Open foundation bank accounts at trusted UAE banks such as Emirates NBD, Mashreq, or ADCB. Navigate Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) requirements with ease.
![]()
Ongoing Compliance
6
Maintain annual filings with the DIFC Registrar, ADGM Registration Authority, or RAK ICC. Complete UAE Economic Substance Regulation (ESR) assessments and submit international reporting as required (e.g., CRS, FATCA).
What Is a UAE Foundation and How Does It Work?
A foundation is a self-owned legal entity without shareholders, blending trust and company features. It holds and manages assets according to its charter and bylaws. With legal personality, a foundation can own property, open accounts, and enter into contracts in its name. It exists indefinitely, unaffected by the death of founders or changes in the council, which helps ensure asset protection, succession planning, wealth management, and long-term control. Establishing a foundation requires a Founder, a Council to manage it, an optional Guardian to oversee compliance, and designated Beneficiaries or specific purposes. Foundations can only be established in designated financial free zones: DIFC (under DIFC Foundations Law No. 3 of 2018), ADGM (under ADGM Foundations Regulations 2017), and RAK ICC (under RAK ICC Foundation Regulations 2019). These laws provide legal protection, confidentiality, and ensure that assets held by the foundation remain separate from the founder’s personal assets.
Why Should You Set Up a Foundation in the UAE?
Foundations in the UAE offer a strategic combination of legal certainty, asset protection, cross-border recognition, and tax efficiency. Whether you register in the DIFC, ADGM, or RAK ICC, here are the key advantages:
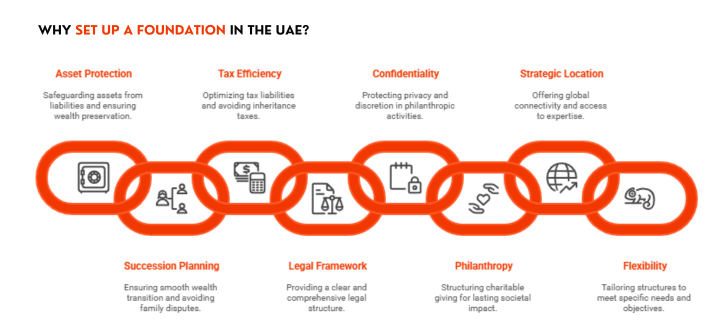
Common Law or Civil Law Flexibility
The UAE allows foundations under multiple legal regimes. DIFC and ADGM operate under English common law, ideal for global enforceability. RAK ICC, meanwhile, offers a civil-law-based framework that’s cost-effective and suitable for regional use cases.
Independent Legal Personality
All UAE foundations are self-owned entities, capable of holding assets, entering contracts, suing or being sued, and operating beyond the founder’s lifetime. This ensures long-term asset continuity and intergenerational control.
Global Asset Consolidation
UAE foundations can legally hold and manage international assets from real estate in London or New York to shares in EU companies, digital tokens, or IP royalties. This allows global families to unify their holdings in one structure.
Real Estate Ownership in the UAE
Foundations registered in DIFC,ADGM or RAK ICC Foundation are recognized by the Dubai Land Department (DLD) and other Emirates for direct property ownership. This avoids nominee arrangements and streamlines inheritance planning for UAE-based real estate.
Reduced Transfer Fees on Property
Foundations transferring UAE property can often benefit from reduced transfer fees as low as 0.125%, compared to the typical 4% if beneficial ownership remains unchanged, making the structure tax-efficient.
Confidential Yet Compliant
While foundation records remain private, the structure is fully compliant with CRS, FATCA, and AML regulations. This ensures confidentiality for founders and beneficiaries without sacrificing legal legitimacy.
Banking and Regulatory Acceptance
Foundations registered in UAE jurisdictions are increasingly favored by international banks, investment platforms, and VCs. Their formal governance structures ease onboarding and due diligence for multi-jurisdictional transactions.
What Legal Documents Are Required to Register a UAE Foundation?
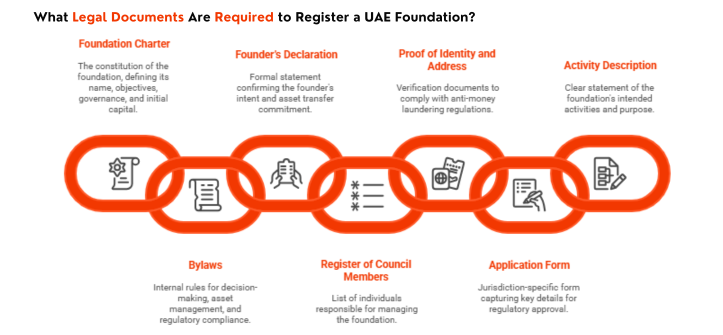
To register a foundation in the UAE, specific documents must be submitted. These form the legal basis of the foundation and establish its legitimacy under the relevant jurisdiction—whether Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM), or Ras Al Khaimah International Corporate Centre (RAK ICC).
1. Foundation Charter
The Foundation Charter, the primary constitutional document of a UAE foundation, defines the foundation’s name, objectives, governance structure, and initial capital. It serves as the core document governing the foundation’s purpose and operations under UAE law.
2. Bylaws
The Bylaws govern the foundation’s internal processes. These set out how the Council Members make decisions, manage assets, and ensure regulatory compliance with DIFC Foundation, ADGM, or RAK ICC requirements.
3. Founder’s Declaration
The Founder’s Declaration formally confirms the Founder’s intent to establish the foundation and transfer assets into it. When the founder is a company (Corporate Founder), corporate registration documents and ownership details must accompany this declaration.
4. Register of Council Members
The Register of Council Members lists all individuals or corporate service providers appointed to manage the foundation. UAE regulations typically require a minimum of two Council Members, who act as fiduciaries responsible for ensuring the foundation adheres to its Charter and Bylaws.
5. Proof of Identity and Address
All founders and Council Members must provide Proof of Identity and Address to comply with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations in the UAE. This includes valid identification documents and verified address information.
6. Application Form
A jurisdiction-specific Application Form must be completed and submitted as part of the registration process. Requirements and formats vary slightly across DIFC, ADGM, and RAK ICC but all ensure that key foundation details are accurately captured for regulatory approval.
7. Activity Description
The Activity Description provides a clear statement of the foundation’s intended lawful activities. This ensures that the foundation aligns with UAE legal requirements and its purpose is properly disclosed to authorities.
How is a UAE foundation governed, and what are its responsibilities?
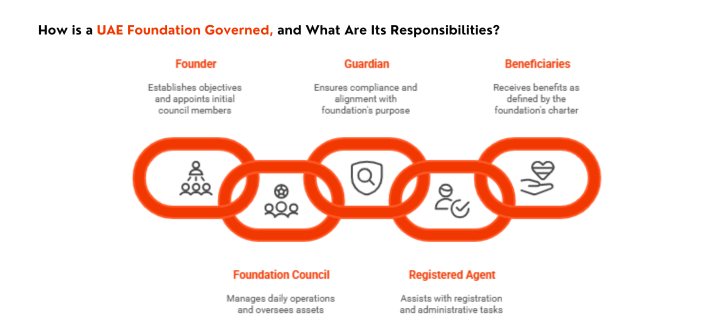
UAE foundations are managed by defined parties with legal roles under DIFC, ADGM, and RAK ICC regulations. Each role supports the separation of ownership and control, a key principle in foundation law.
Founder
The founder is the person or company that creates the foundation. They define its objectives and appoint the initial council. The founder may also transfer assets to the foundation and choose to serve as a council member, but cannot act as both council and guardian.
Foundation Council
The foundation council is the main governing body. It manages daily operations, oversees assets, and enforces the foundation’s charter and bylaws. In most UAE jurisdictions, at least two council members are required. These can be individuals or corporate council members licensed corporate service providers appointed to act in a fiduciary capacity. The founder may join the council to retain influence, though additional members are often added for oversight and continuity.
Guardian
The guardian ensures the foundation council acts in line with the foundation’s purpose. This role is mandatory for charitable foundations in DIFC, ADGM, and RAK ICC, and optional for private foundations. Guardians may be individuals or licensed firms acting as corporate guardians. They cannot serve on the foundation council and often hold veto powers to block non-compliant decisions.
Registered Agent
This is a third-party firm or individual that helps register the foundation. RAK ICC requires a registered agent. DIFC and ADGM Foundation do not, but many founders still appoint one for support with filings and communication with the registrar and to provide the office address.
Beneficiaries
These are individuals or entities named to receive benefits from the foundation. Their rights depend on what the charter and bylaws specify. In some setups, the founder can also be a beneficiary while still maintaining asset separation. Know more about beneficiary here.
What Can a UAE Foundation Be Used For and What Assets Can It Hold?
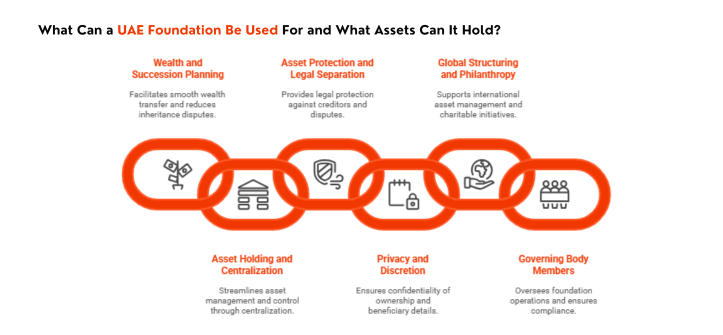
A UAE foundation is designed to hold, manage, and protect a wide range of assets for long-term goals. These include succession planning, wealth protection, and international structuring.
1. Wealth and Succession Planning
- Foundations allow families to transfer wealth without court intervention. They reduce inheritance disputes by defining clear rules for beneficiaries. Assets remain within the structure, unaffected by the founder’s death or legal issues.
1
2. Asset Holding and Centralization
A foundation can consolidate various asset types into one legal entity. These include:
- Real Estate: UAE foundations can own residential, commercial, or industrial properties. In Dubai and other emirates and even worldwide, properties held through a DIFC foundation benefit from a reduced transfer fee of 0.125%.
- Company Shares: Foundations can hold equity in UAE or international companies and retain full shareholder rights.
- Cash and Investments: Multi-currency bank accounts, savings, and managed investment portfolios can be controlled by the foundation.
- Intellectual Property: Ownership of patents, trademarks, or digital assets can be centralized under the foundation for control and royalty management.
- Family Businesses: Foundations can hold operating businesses or equity interests, offering business continuity beyond the founder’s lifetime.
2
3. Asset Protection and Legal Separation
Assets held by the foundation are legally separate from the founder. This protects them from creditors, legal claims, or disputes, provided the structure is used correctly.
3
4. Privacy and Discretion
Ownership and beneficiary details are not public in most UAE jurisdictions, providing confidentiality while staying compliant with international reporting obligations.
4
5. Global Structuring and Philanthropy
Foundations are often used to hold assets outside the UAE such as offshore companies, US real estate, or EU securities under one structure. They also support ongoing charitable initiatives through structured giving.
What Are the Legal Requirements to Establish a UAE Foundation?
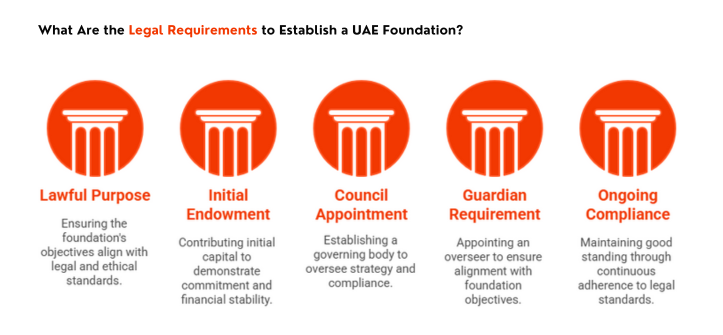
To set up a UAE foundation, founders must satisfy core legal and regulatory conditions. These include jurisdictional alignment, proper documentation, and ongoing governance standards.
Purpose Must Be Lawful and Defined
The foundation must be created for a legitimate purpose such as family succession, asset protection, or charitable giving. A clearly written objective is required to avoid regulatory rejection or future disputes.
Initial Endowment Must Be Contributed
A minimum capital contribution is required upon formation. DIFC, ADGM, and RAK ICC set their own thresholds, usually ranging from AED 1,000 to AED 5,000. The funds must be transferred into a foundation-held bank account.
Appointing Foundation Council Members
At least one individual must be appointed to the foundation council. This body governs the foundation’s strategy, ensures compliance, and manages operations according to the charter and bylaws.
Guardian Requirement (Where Applicable)
For certain structures, especially charitable foundations, a guardian is mandatory. This role exists to oversee council decisions and ensure alignment with the foundation’s stated objectives.
Ongoing Legal Compliance
After registration, the foundation must file annual reports, maintain internal records, and report changes in council membership or other key governance structures to the relevant authority.
Tax Benefits for Family Foundations in the UAE
UAE foundations provide significant tax advantages:
- Potential for tax neutrality under certain conditions
- Eligibility for treatment as an unincorporated partnership, passing tax liabilities to beneficiaries
- Zero personal income tax on foundation beneficiaries
- No corporate income tax for qualifying foundations
- Reduced transfer fees (0.125% vs 4% for real estate)
- Estate tax exemptions with no inheritance taxes
- Capital gains tax relief on foundation asset sales
Different Types of Foundations
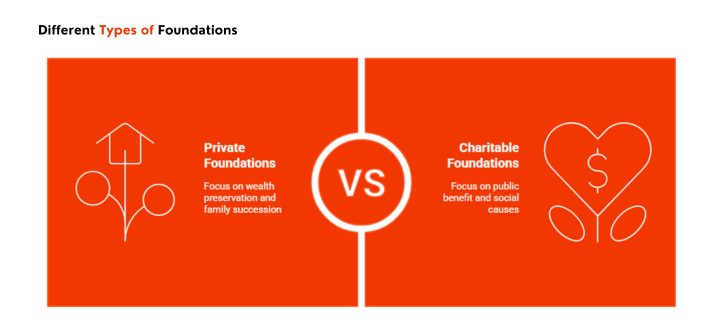
UAE law recognizes several foundation types, each serving distinct purposes and objectives:
Private Foundations
Established for specific families or individuals, private foundations focus on wealth preservation and succession planning. They maintain privacy and confidentiality while supporting multiple generations. Private foundations provide the most flexibility for family wealth management. They can distribute income, accumulate assets, and make investments based on family needs.
Charitable Foundations
Created to serve public or charitable purposes, these foundations support community initiatives and social causes. They may provide tax advantages in some jurisdictions and boost corporate reputation. Charitable foundations must serve recognized charitable purposes. They cannot provide private benefits to founders or their families.
Why Register a Foundation in the UAE
Political Stability
The UAE provides a stable political environment with consistent policies. This stability protects foundation assets and maintains operational continuity.
Strong Legal Framework
UAE foundation laws provide comprehensive asset protection and governance structures. Courts enforce foundation rights and protect beneficiary interests.
Business-Friendly Environment
The UAE welcomes international businesses and investors. Minimal bureaucracy and efficient processes support foundation operations.
Tax Efficiency
Zero personal income tax and minimal corporate obligations make the UAE attractive for wealth structuring. Tax treaties provide additional benefits for international planning.
Strategic Location
The UAE connects global markets and facilitates international business. Time zone advantages support worldwide investment management.
Professional Services
Dubai and Abu Dhabi provide world-class legal, accounting, and financial services. Experienced professionals support foundation management and compliance.
Banking Infrastructure
UAE banks offer sophisticated services for foundation accounts. International banking relationships support global asset management.
Regulatory Recognition
UAE authorities recognize foundations for property ownership, business registration, and financial services. This recognition provides operational certainty.
Governance and Reporting Standards for UAE Foundations
UAE foundations are subject to statutory governance and reporting obligations to ensure transparency, compliance, and alignment with their stated purposes.
Annual Reporting Obligations
- Confirmation Statement: Foundations must file an annual confirmation statement with the registrar, affirming that all information is up to date.
- Financial Statements: Regular preparation of financial statements is mandatory. The requirement to submit audited financial statements varies by jurisdiction and the foundation’s activities.
- Record Maintenance: Accurate and up-to-date records of all foundation activities, financial transactions, and council decisions must be maintained.
Best places to set up a foundation in UAE
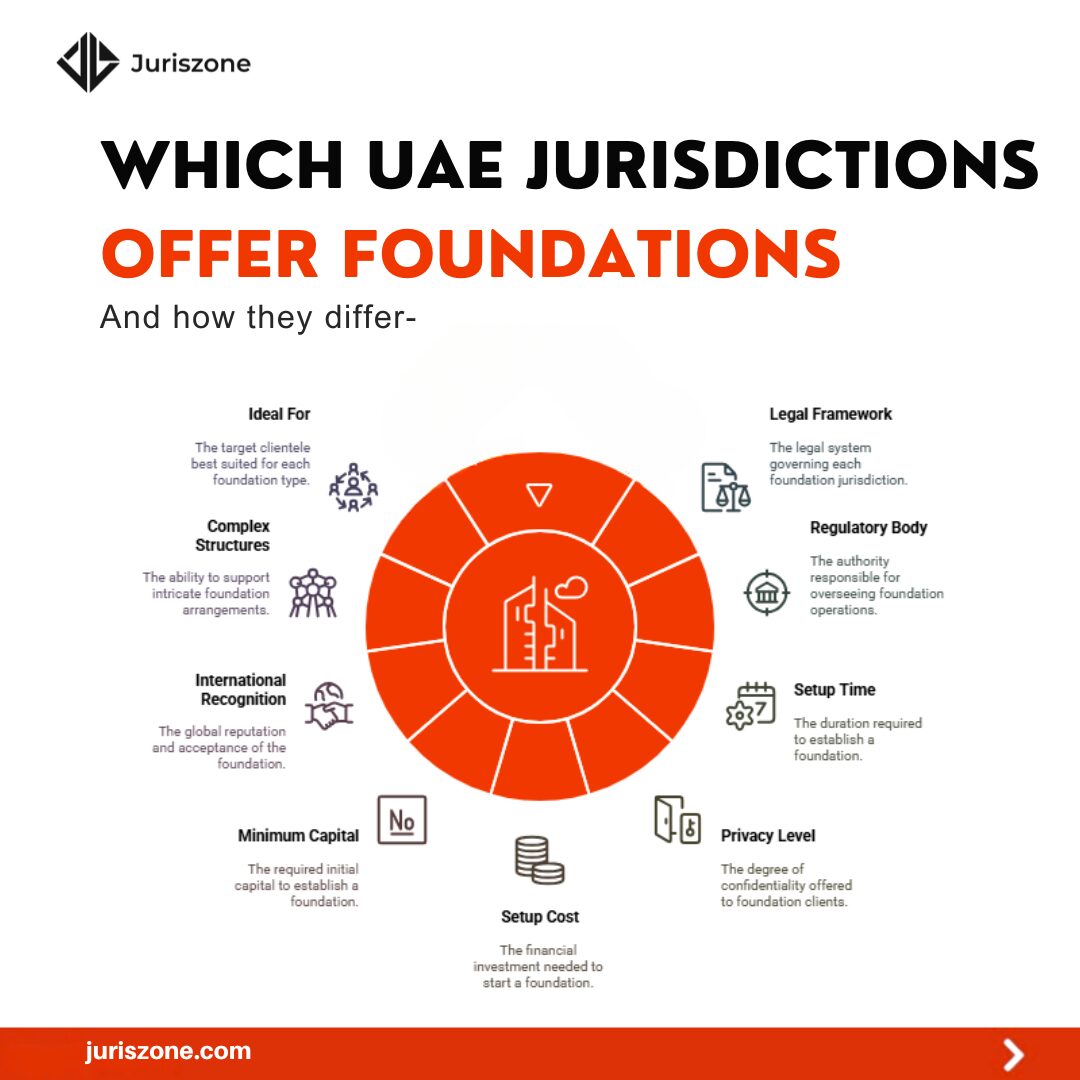
UAE foundation law operates under three main jurisdictions: Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC), Abu Dhabi Global Market (ADGM), and Ras Al Khaimah International Corporate Centre (RAK ICC). Each jurisdiction provides distinct legal frameworks.
DIFC foundations are separate legal entities with perpetual succession under DIFC Law No. 3 of 2018. The DIFC framework provides English common law protections, comprehensive governance, and strong asset protection, ensuring global enforceability and legal certainty.
ADGM foundations follow the ADGM Foundations Regulations 2018. These regulations create a flexible foundation structure based on common law principles. The framework supports complex international wealth planning strategies.
RAK ICC foundations operate under Federal Law No. 2 of 2015. This civil law framework provides cost-effective foundation solutions. The structure appeals to small and medium enterprises seeking affordable asset protection.
| Feature | DIFC Foundation | ADGM Foundation | RAK ICC Foundation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legal Framework | English Common Law | English Common Law | UAE Civil Law |
| Regulatory Body | DIFC Authority | ADGM Registration Authority | RAK ICC |
| Setup Time | 1-2 weeks | 1-2 weeks | 1-2 weeks |
| Privacy Level | High | High | Moderate |
| Setup Cost | Higher | Higher | More Affordable |
| Minimum Capital | No requirement | No requirement | No requirement |
| International Recognition | Excellent | Excellent | Good |
| Complex Structures | Supported | Supported | Limited |
| Ideal For | HNWIs, Complex Planning | International Families | SMEs, Cost-Conscious |
Finalizing Your UAE Foundation: What Comes Next
Establishing a UAE foundation is a strategic move for asset protection, succession planning, and cross-border wealth management. Once you’ve reviewed the legal framework, governance structure, and jurisdictional options, the next step is professional execution.
Our Services Cover:
- Selection of the right jurisdiction (DIFC, ADGM, or RAK ICC)
- Drafting compliant charters, bylaws, and founder declarations
- Coordination with regulatory authorities and registrar offices
- Foundation bank account setup and asset transfer advisory
- Ongoing legal compliance, filings, and audit support
- Structuring for international holdings and multi-jurisdictional families
Contact Juriszone Today To Begin Trust & Foundation Setup In UAE
FAQs About Foundation Setup in Dubai
UAE foundations can own and manage international assets, including real estate, shares, and intellectual property in the UK, EU, and US. This structure centralizes global asset management and simplifies estate planning.
UAE foundations can own and manage international assets, including real estate, shares, and intellectual property in the UK, EU, and US. This structure centralizes global asset management and simplifies estate planning.
A foundation is governed by a Founder, a Foundation Council to manage daily operations and Beneficiaries who receive benefits. Sometimes a Guardian is appointed to ensure proper oversight.




